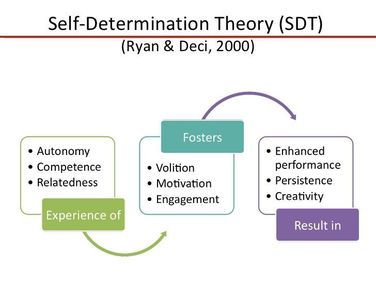
This is true for students as well as for ourselves as teachers. Essentially as humans, we want to feel like we have some choice we want to feel like we can do it and we want to feel connected. Hit those three needs and you are developing intrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation leads to engaging in a task voluntarily out of pure enjoyment, interest and excitement. This differs from extrinsic motivation where we might complete a task out of fear, or in order to benefit from a reward of some kind.
Plan to motivate
|
Let’s say you love reading: you get to choose the book, the pace you go at, the author etc.
Autonomy. Tick. ✅ You understand it, you feel like you’re in the story, you're learning about the characters or the topic, you get it. Competence. Tick. ✅ You connect to the characters, or you love discussing the book with other avid reader friends. Relatedness. Tick. ✅ You are intrinsically motivated to read. The same can be done for any activity you choose freely to engage in out of pure interest and enjoyment.
Now think about our last online lesson. Did we plan activities for our students that meet those needs? Probably not! Why? Because it is not easy! This online teaching stuff is a steep learning curve and most of us are just trying to keep our heads above water and not lose the plot entirely! I’m with you.
So… how can we transfer what we know about self-determination theory to the online classroom in order to maintain intrinsic motivation among our students and ourselves, as teachers? It can feel a lot more difficult to hit those three basic psychological needs from our own sitting room, without the smiling (and bewildered!) faces of our students in front of us. But with some modifications to our planning we can get there. |
|
My top four tips for motivation
- Let them see you: If you are using video software for your classes, this is great. Smile, be silly, talk about what you are doing in this lockdown period, show them your favourite hat, or your new hairstyle. Whatever. Just be yourself and chat to them. This builds connections and maintains the relationships. If you are not allowed to use video software, then make a few short youtube videos like these ones. They don’t have to be public if you don’t want that but the kids miss you. They want to see your face. And unbelievably, they find the most mundane things about our lives super interesting. Remember, they think we don’t exist outside the school walls so showing them your favourite plant in your apartment can blow their minds!
- Get them moving: They are sitting all day… alllll day. Just as we are. So do activities that get them out of their seats. As language teachers this is a chance to give more comprehensible input: “Find me something small and green in your house, you have 1 minute” or “stand up, add these numbers and sit when you have the answer”. Or ‘Simon says’. Anything that gets them moving, keeps them engaged, keeps them listening to your input and builds relationships. Even better if you do the activity too. They’ll be smiling and giggling at you trying too. This also builds their competence as they are listening, understanding and following along. The competence is developed even further if you make a big deal out of the cool item they found, or awesome t-shirt they've on.
- Lower the expectations: Online teaching and learning is simply not the same as the real classroom. Lower your learning objectives. Actively take things out of your units & curriculum. This is the time to be creative and do cool new things. Don’t worry about ‘being behind’... Behind who?? Or behind what?? We are all in this together. Now is not the time to over-burden with loads of exercises. Focus on motivation, not examination. Plan your lesson with detailed steps. Then when you are done, take one step out. Put it in the next lesson. This helps their competence as they feel like they are making it to the end each day. What about those learners who want extension activities? No worries. Have some youtube links ready or some extra reading or even better, some creative project to work on.
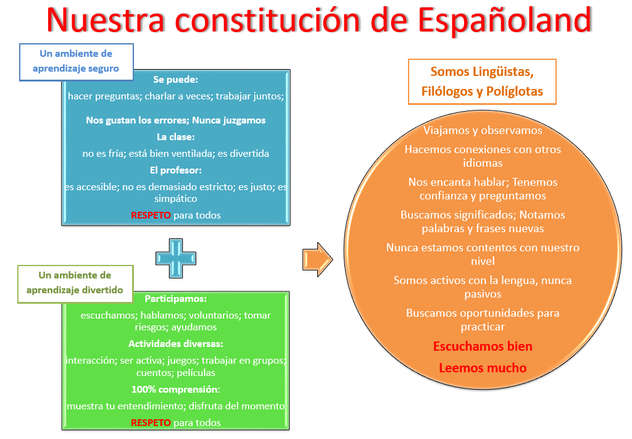
- Open up the choices: Autonomy is not about going off on your own tangent every time. It is about choice, self-direction and having some say in where things are going. Ask the students to vote on the tasks for the next class, give them 3 or 4 options of ways to show their learning. Let them be creative and make videos about topics you are doing. Give them the creative license and autonomy and you will be amazed and what they give you back. Especially those quiet students who say nothing in the video chat sessions.
Keep the conversation going
Please leave your comments below!
#TogetherWeAreStronger #MotivationNotExamination









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed